BILLY Talks
Part 01: Tech Vocab 101
Tech Speak

HTTP
... HyperText Transfer Protocol ...
HTTP is the underlying protocol used by the World Wide Web and this protocol defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands.
HTTPS
... HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure ...
Basically, it is the secure version of HTTP. Communications between the browser and website are encrypted by Transport Layer Security (TLS), or its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
URL
... A uniform resource locator (URL) ...
A uniform resource locator (URL) is the address of a resource on the Internet. A URL indicates the location of a resource as well as the protocol used to access it.
URL Structure
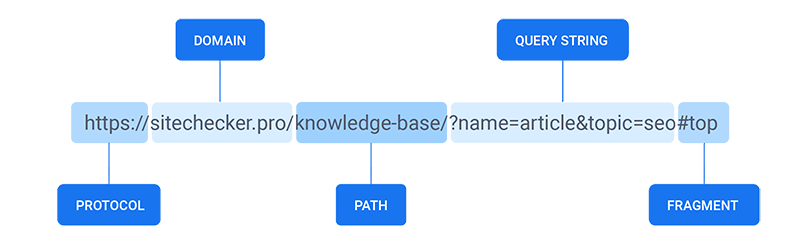
- Protocol
- Sub-Domain (optional)
- Domain
- Path
- Query String (optional)
- Fragment (optional)
URL's. Are they friendly?


IP Address
... A unique address that identifies a device on the Internet or a local network ...
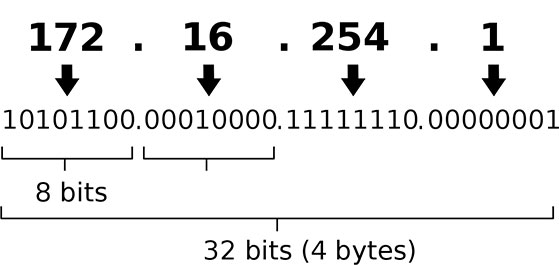
An IP address, or simply an "IP," allows a system to be recognized by other systems connected via the Internet protocol. There are two primary types of IP address formats used today — IPv4 and IPv6
IP Structure
IPv4 address in dotted decimal notation
NAT
... Network Address Translation ...
Designed for IP address conservation. It enables private IP networks that use unregistered IP addresses to connect to the Internet. NAT operates on a router, usually connecting two networks together, and translates the private (not globally unique) addresses in the internal network into legal addresses, before packets are forwarded to another network.
Why NAT matters?
As we work with providers of 3rd party data who claim to be able to match individuals in their homes, offices and wherever else an IP address is present in requests to various web sites and applications, we need to be aware that this is not entirely possible with "just" IP address ..
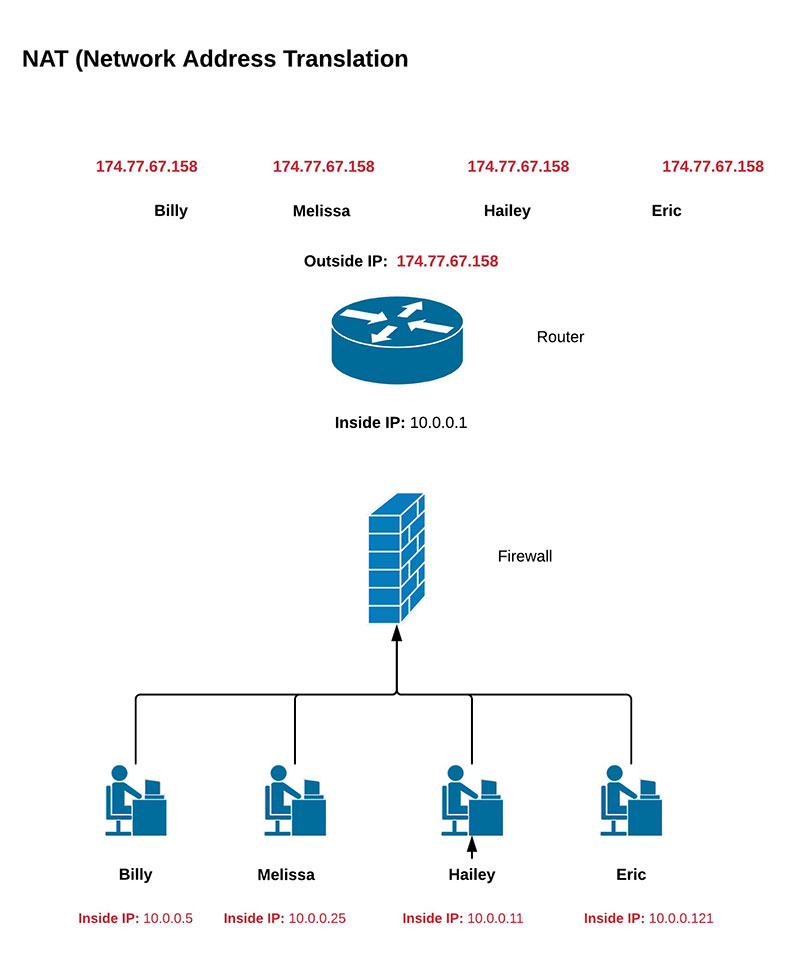
Ideally, we are asking some questions about how this match is done. Are they tying a companies IP address to individuals inside by some other identifier?
Something like:
| IP | |
|---|---|
| 174.77.67.158 | billy@deferousa.com |
| 174.77.67.158 | mercier@deferousa.com |
| 174.77.67.158 | hcrider@deferousa.com |
| 174.77.67.158 | ebrandt@deferousa.com |
Domain Registrar
... A domain name registrar is a business that handles the reservation of domain names ...
Examples
DNS
... Domain Name System ...
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. Humans access information online through domain names, like nytimes.com or espn.com. Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
DNS Resource Records
... Multiple types of records. ...
A Record
An A record maps a domain name to the IP address (Version 4) of the computer hosting the domain. ... A Records are the simplest type of DNS records, and one of the primary records used in DNS servers.
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| A | deferousa.com. 886 IN A 23.185.0.1 |
CNAME Record
CNAME records can be used to alias one name to another. ... An A record for example.com pointing to the server IP address. ... A CNAME record must always point to another domain name, never directly to an IP address.
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| CNAME | www.deferousa.com. 527 IN CNAME live-defero-usa.pantheonsite.io. |
MX Record
Mail Exchange (MX) records are DNS records that are necessary for delivering email to your address. In simple DNS terms, an MX record is used to tell the world which mail servers accept incoming mail for your domain and where emails sent to your domain should be routed to.
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| MX | deferousa.com. 3599 IN MX 10 mx2-us1.ppe-hosted.com. deferousa.com. 3599 IN MX 0 mx1-us1.ppe-hosted.com. |
TXT Record
TXT records are a type of Domain Name System (DNS) record that contains text information for sources outside of your domain. You add these records to your domain settings. You can use TXT records for various purposes. Google uses them to verify domain ownership and to ensure email security.
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| TXT | deferousa.com. 3599 IN TXT "v=spf1 a mx a:dispatch-us.ppe-hosted.com include:spf.protection.outlook.com ip4:107.170.213.95 include:e2ma.net ip4:98.174.248.51 ip4:23.253.130.74 -all" |
TTL
... Time to Live ...
TTL (Time to Live) is a setting for each DNS record that specifies how long a resolver is supposed to cache (or remember) the DNS query before the query expires and a new one needs to be done
SPF Record
... Sender Policy Framework ...
Sender Policy Framework is an email authentication method designed to detect forging sender addresses during the delivery of the email. SPF alone though is limited only to detect a forged sender claimed in the envelope of the mail which is used when the mail gets bounced.
It's just a DNS TXT record
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| TXT | deferousa.com. 3599 IN TXT "v=spf1 a mx a:dispatch-us.ppe-hosted.com include:spf.protection.outlook.com ip4:107.170.213.95 include:e2ma.net ip4:98.174.248.51 ip4:23.253.130.74 -all" |
Common file transfer protocols
FTP
... File Transfer Protocol ...
FTP is a protocol designed for transferring files over the Internet. Files stored on an FTP server can be accessed using an FTP client, such as a web browser, FTP software program, or a command line interface.
SFTP
... Secure File Transfer Protocol ...
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a secure version of File Transfer Protocol (FTP), which facilitates data access and data transfer over a Secure Shell (SSH) data stream. It is part of the SSH Protocol. This term is also known as SSH File Transfer Protocol.
SSH
... Secure Shell or Secure Socket Shell ...
A network protocol that gives users, particularly system administrators, a secure way to access a computer over an unsecured network. SSH also refers to the suite of utilities that implement the SSH protocol.
API
... Application Programming Interface ...
Application Programming Interface (API) In basic terms, APIs just allow applications to communicate with one another. When people speak of “an API”, they sometimes generalize and actually mean “a publicly available web-based API that returns data, likely in JSON or XML”.
SDK
... Software Development Kit ...
The SDK brings together a group of tools that enable the programming of mobile applications. This set of tools can be divided into 3 categories: SDKs for programming or operating system environments (iOS, Android, etc.)
Cookie
... Small files which are stored on a user's browser. ...
A computer “cookie” is more formally known as an HTTP cookie, a web cookie, an Internet cookie or a browser cookie. The name is a shorter version of “magic cookie,” which is a term for a packet of data that a computer receives and then sends back without changing or altering it.
Session
... Small files which are stored on a user's browser ...
The difference between a session and a cookie is that session data is stored on the server, whereas cookies store data in the visitor's browser. ... Data stored in cookie can be stored for months or years, depending on the life span of the cookie. But the data in the session is lost when the web browser is closed.
Few Examples
Cookie example
has_seen_banner=yes
registerd=false
adkey=DEFGGL
Session example
JSESSIONID=a61ea0f1-9c2c-11e9-b86d-6b8c28b90065;
PHPSESSIONID=a61ea0f1-9c2c-11e9-b86d-6b8c28b90065;
app_sess=13453343
Tracking Pixel
... A small piece of code placed on a website for tracking purposes ...
This can be in the form of a simple HTML image tag:

... anyone notice the query string above? ...
Or in the form of complex Javascript:
SQL
... Structured Query Language ...
Pronounced either see-kwell or as separate letters. SQL is a standardized query language for requesting information from a database.
THE END
... Thanks Everyone!!